| Tetrapodomorphs Fossil range: late Early Devonian - Recent | |
|---|---|
 The basal tetrapodomorph Tiktaalik. | |
| Scientific classification
| |
|
Class |
|
|
Subclass |
Tetrapodomorpha |
|
Subgroups |
|
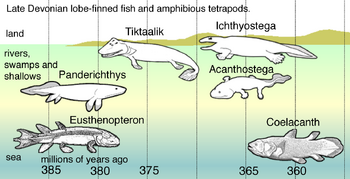
In Late Devonian vertebrate speciation, descendants of pelagic lobe-finned fish — like Eusthenopteron — exhibited a sequence of adaptations:
•Panderichthys, suited to muddy shallows;
•Tiktaalik with limb-like fins that could take it onto land;
•Early tetrapods in weed-filled swamps, such as;
•Acanthostega, which had feet with eight digits,
•Ichthyostega with limbs.
Descendants also included pelagic lobe-finned fish such as coelacanth species.
Tetrapodomorpha is a clade of vertebrates, consisting of sarcopterygians with a number of features of tetrapods. Primitive forms, like Tiktaalik, have been referred to as "fishapods" by their discoverers, since they were half-fish half-tetrapods, at least in appearance.
Tetrapodomorpha contains the true tetrapods and several groups of related lobe-finned fishes, collectively known as the osteolepiforms.
Among the characters defining the tetrapodomorphs are modifications to the fins, notably a humerus with convex head articulating with the glenoid fossa (the socket of the shoulder joint).
Tetrapodomorph fossils are known from the early Devonian onwards, and include Osteolepis and Panderichthys.
Taxonomy and phylogeny[]
- Class Sarcopterygii
- Subclass Tetrapodomorpha
- Kenichthys
- Order Rhizodontida
- Superorder Osteolepidida (or Osteolepiformes)
- Family Osteolepidae
- Family Tristichopteridae
- Family Megalichthyidae
- Megalichthys
- Family Canowindridae
- (unranked) Elpistostegalia
- Order Panderichthyida
- Tiktaalik
- Livoniana
- Metaxygnathus
- Ventastega
- Superclass Tetrapoda
- Subclass Tetrapodomorpha
- After Benton, 2004 [1]:
References[]
- Mikko Haaramo. "Tetrapodomorpha - Terrestrial vertebrate-like sarcopterygians". http://www.fmnh.helsinki.fi/users/haaramo/Metazoa/Deuterostoma/Chordata/sarcopterygii/tetrapodomorpha.htm. Retrieved on 6 April.
- P. E. Ahlberg and Z. Johanson (1998). "Osteolepiforms and the ancestry of tetrapods". Nature 395 (6704): 792–794. doi:.
- Michel Laurin, Marc Girondot and Armand de Ricqlès (2000). "Early tetrapod evolution". TREE 15 (3). http://www.ese.u-psud.fr/epc/conservation/Publi/abstracta/AE_TREE2000.pdf.